
Wave energy's potential for India's sustainable future
India needs to shift towards sustainable energy sources. Wave energy, a vital source in this transition, has yet to be harnessed. India has a vast coastline, making the potential for wave power affordable. Financial incentives, innovation and public-private partnerships are needed to promote wave energy development in India
 Wave energy is a clean and sustainable source that can help reduce India's dependence on fossil fuels. Image: Shutterstock
Wave energy is a clean and sustainable source that can help reduce India's dependence on fossil fuels. Image: Shutterstock
India needs to expedite its transition towards cleaner and sustainable energy sources to reduce the risks associated with reliance on fossil fuels. This transition faces a significant hurdle: Ensuring the availability of clean electricity around the clock every day of the year. Wave and tidal energy can be vital in addressing this challenge and contribute to India's energy mix.
Wave energy is a clean and sustainable source that can help reduce India's dependence on fossil fuels. By harnessing the power of ocean waves, wave energy technologies can generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other harmful pollutants. This makes wave energy a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional energy sources.Also read: India can not only be the world's richest, but also the most inclusive economy by 2047: Rajiv Shah
What is wave energy, and what potential it has for India?
Wave energy, a renewable energy source, can be harnessed from water movement near the sea’s surface. India's vast coastline of approximately 7,517 km provides an ideal platform for developing wave energy resources. India receives significant wave energy throughout the year, especially along the western coast. According to the IIT Madras–CRISIL Report of 2014, India's theoretical potential for wave power is 40 GW, and its potential for tidal power is 12 GW.Green technology, such as wave and tidal energy, can boost economic growth, energy security, job creation, and global export. Wave energy can power various establishments such as oil & gas, defence bases, ports & harbours, and islands. It also has potential applications such as sea surveillance, coral reef regeneration, navigational buoys, and desalination. Producing green hydrogen from wave energy can also help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.Also read: Decarbonisation may impact Indian household spending and jobs: McKinsey & Company report
Wave energy has the potential to be used in various ways to tackle climate change in India, including renewable energy generation, decentralised power generation, off-grid power generation, energy storage, and desalination. For instance, green hydrogen can be used in steel production to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
While wave energy is still in the early stages of development in India, it has enormous potential as an alternative energy source. However, there are technical and financial challenges that need to be overcome. With the right policies and incentives, wave energy can significantly influence India's transition towards a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.Also read: UN urges 'complete transformation' of global energy system to fight climate change
Wave energy has enormous potential in India, and leveraging it can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve energy access, and promote sustainable development. India can benefit from this clean and renewable energy source by developing policies and incentives to encourage growth.
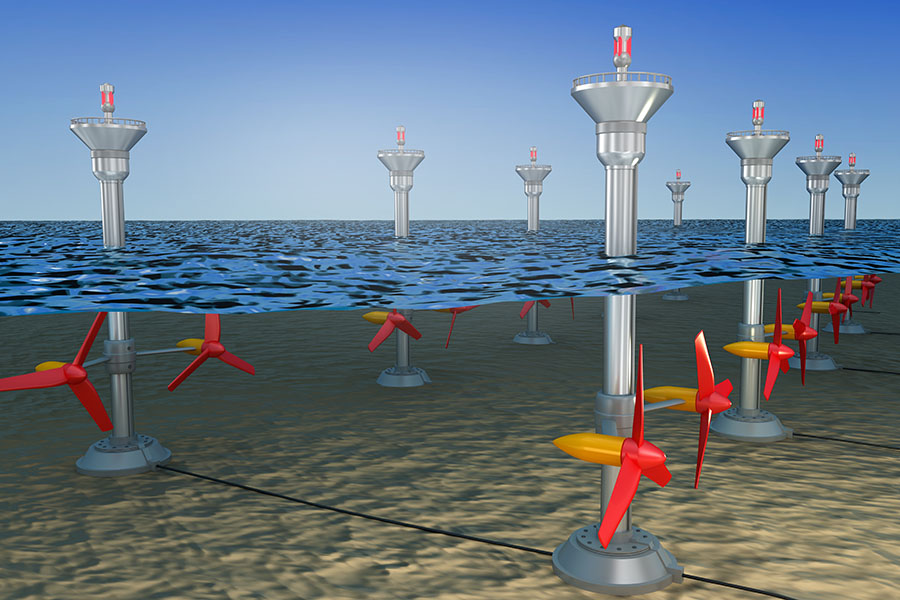
Showcasing PAWEC
Point Absorber Wave Energy Converter (PAWEC) is a device designed to convert the energy of ocean waves into electricity. A point absorber is a typical float oscillating body, which usually utilises a submerged or floating body to trap the oscillating force of the wave, which converts the kinetic energy of ocean waves into electrical energy using a buoyant structure.The device works in four basic steps. Firstly, the buoyant structure is designed to absorb the motion of ocean waves, which causes the system to move up and down. This motion is then converted into mechanical energy. Secondly, the mechanical energy generated by the wave absorption is transmitted to a power take-off (PTO) system, which is responsible for converting the mechanical energy into rotational energy. Thirdly, the rotational energy produced by the PTO system drives an electrical generator, which converts the rotational energy into electrical energy. Finally, a control system monitors and adjusts the device's performance to ensure it operates safely and efficiently.Also read: Challenges of realising a global carbon price
PAWEC requires careful design and monitoring to ensure it operates within safe limits and maximises energy production. It is a floating device that can be used to generate electricity in remote areas where traditional power sources are unavailable. The Point Absorber Wave Energy Converter provides a promising solution for converting the energy of ocean waves into electricity. Its four-step process of wave absorption, power take-off, electrical generation, and control system ensures efficient and safe operation, making it a viable option for clean energy production.
Policy Recommendations for Wave Energy Development in India
The government can implement several policies to promote wave energy development in India. The first is to provide financial incentives such as feed-in-tariffs (FITs) to encourage the deployment of wave energy projects. This would offer a fixed rate for each unit of electricity generated, providing investors with long-term revenue certainty.Another policy option is to impose Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPOs) on electricity distribution companies, requiring them to purchase a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources, including wave energy. This would create a market for renewable energy technologies and drive demand for wave energy.Also read: Without collaboration, green transition 'delayed by decades': IEA
In addition, the government can provide funding for Research and Development (R&D) in wave energy technologies to promote innovation, reduce costs, and improve the efficiency of wave energy devices. They can also establish clear regulations and policies related to wave energy, including environmental impact assessments, grid connectivity, and permitting processes. This would give developers greater clarity and certainty, reducing the risk of investing in wave energy projects.
Finally, the government can facilitate public-private partnerships to promote collaboration between the public and private sectors in developing wave energy projects. This would help leverage both sectors' expertise and resources to accelerate the deployment of wave energy technologies. Implementing these policies would create a supportive environment for wave energy development in India, attracting investment and promoting sustainable energy development.
Sai Arun Kiran Karthik Sunkara is a Senior Academic Associate, Strategy & Leadership Domain, ISB Hyderabad.
Anjal Prakash is an Associate Professor (Research) and Research Director- at the Bharti Institute of Public Policy at ISB. He contributes to IPCC reports.
[This article has been reproduced with permission from the Indian School of Business, India]
Post Your Comment

















